Peaky blinder stars
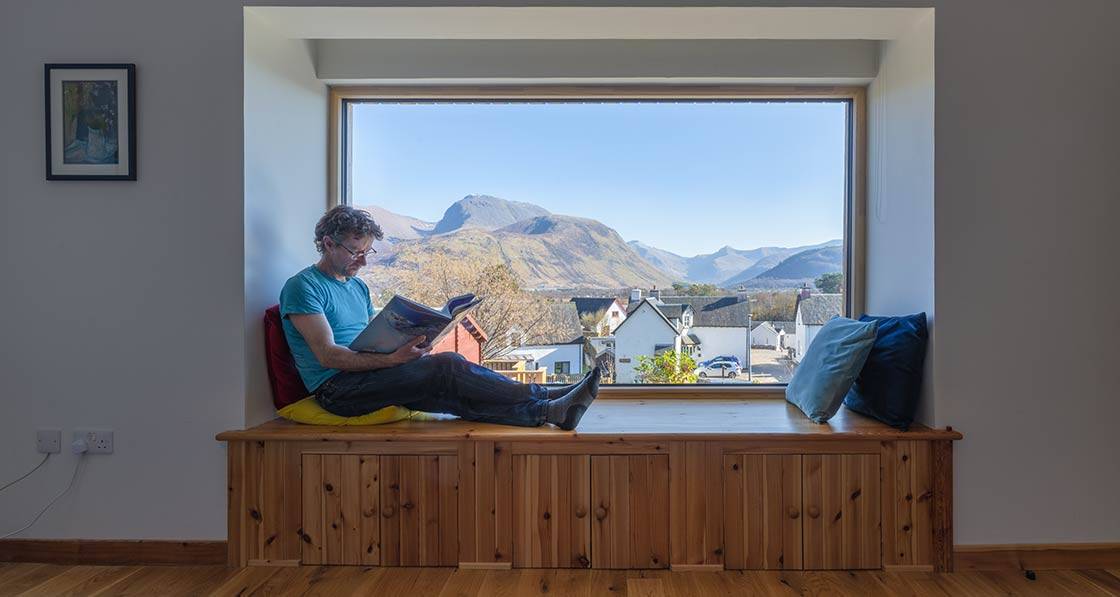
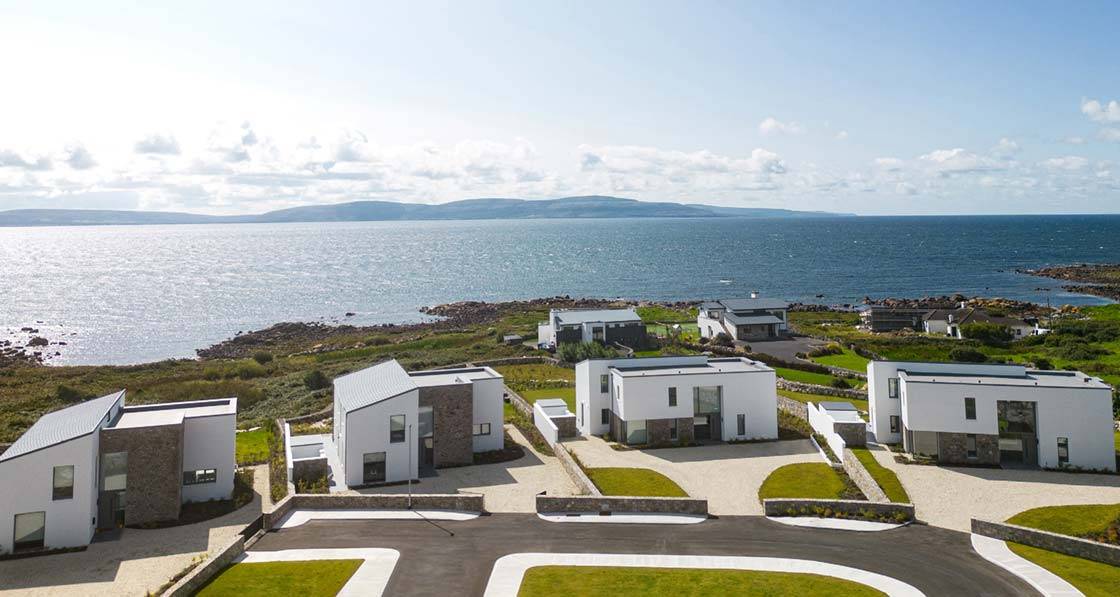
From frozen tea to thermal bliss: energy specialist Esmond Tresidder transformed his leaky 1970s Highland home into one of the highest performing retrofits ever featured in these pages, combining academic knowledge with hands-on retrofit innovation to create a comfortable, healthy family haven with breathtaking views of Ben Nevis, proving that even Scotland’s most challenging climates are no match for passive house principles.