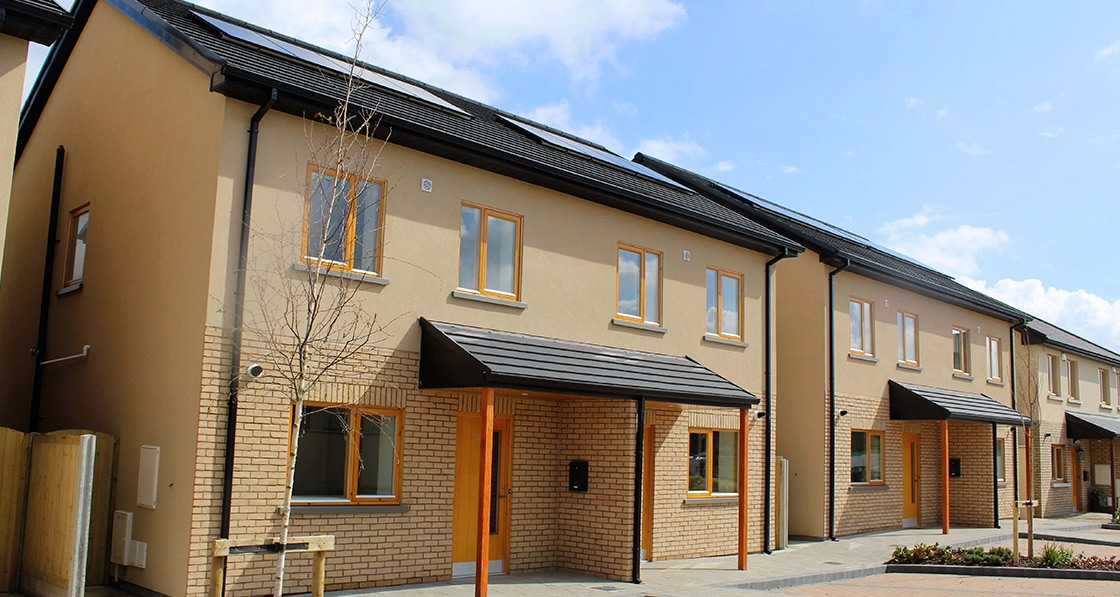
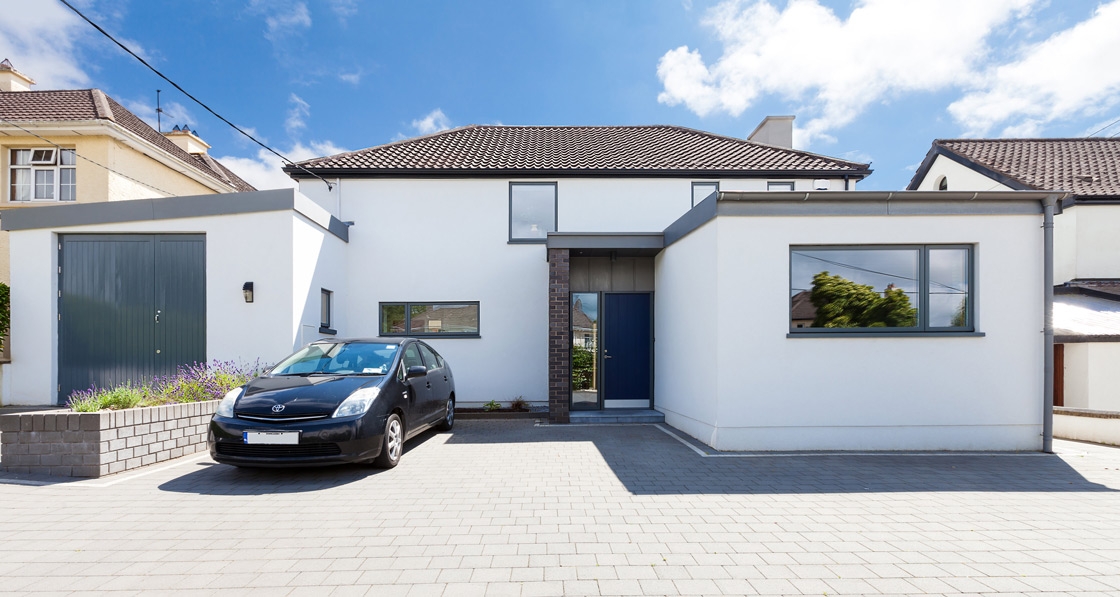
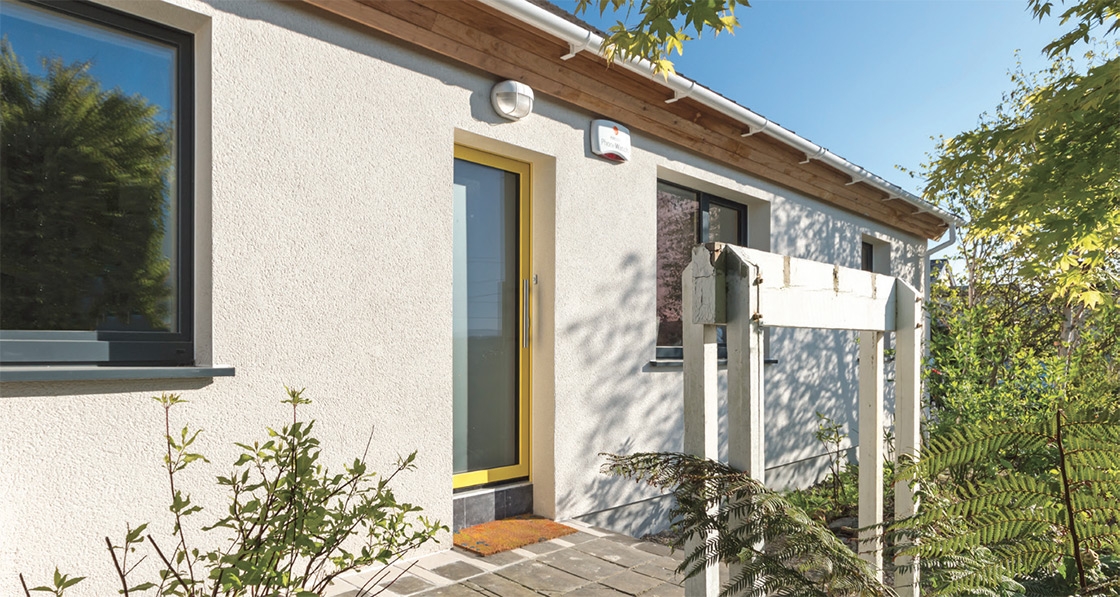
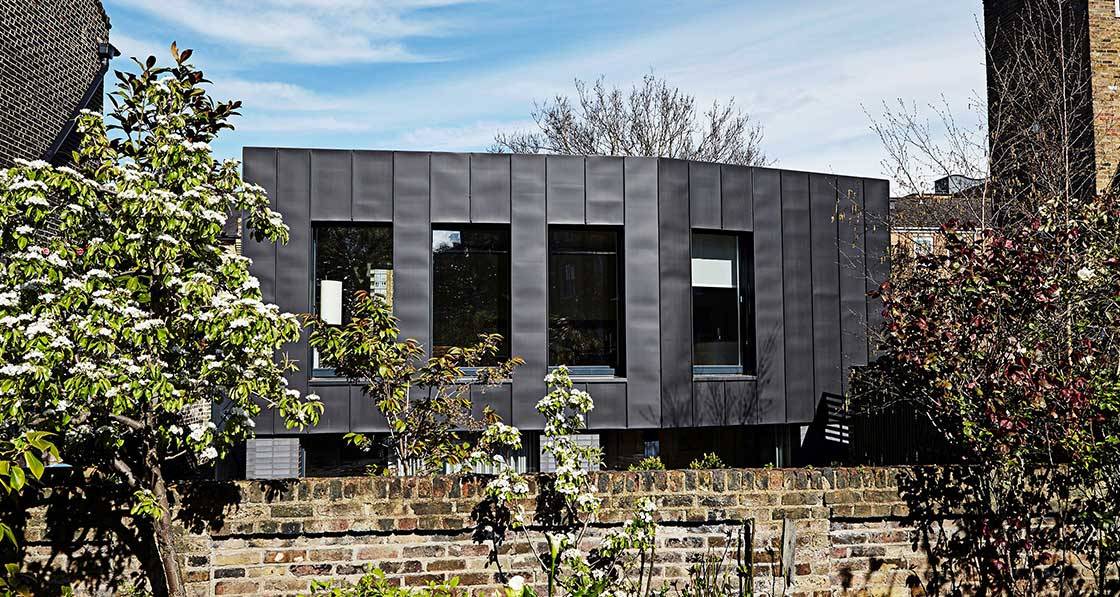
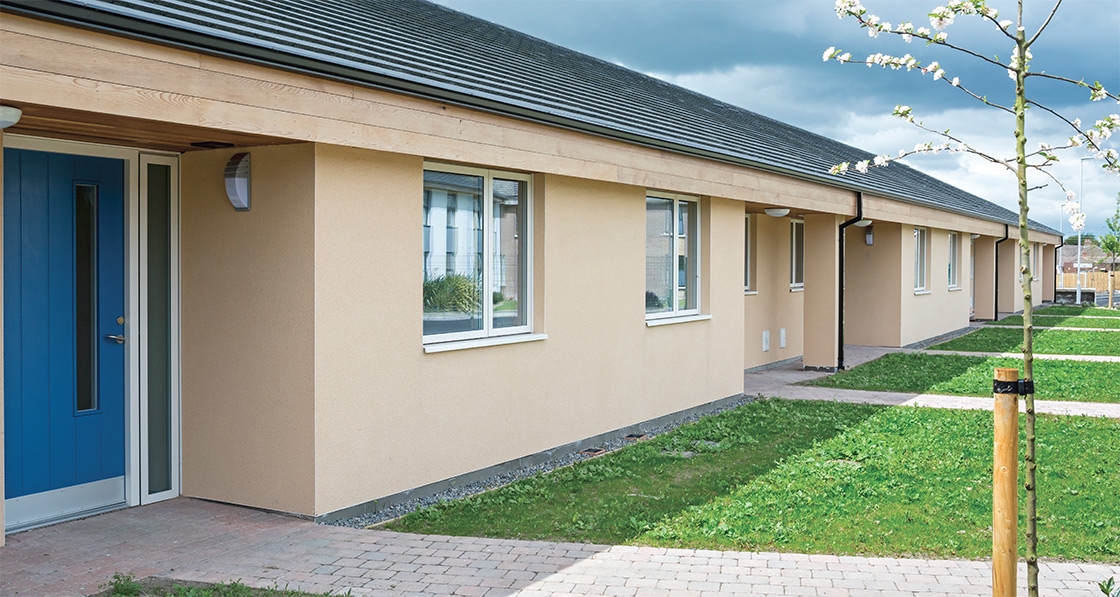
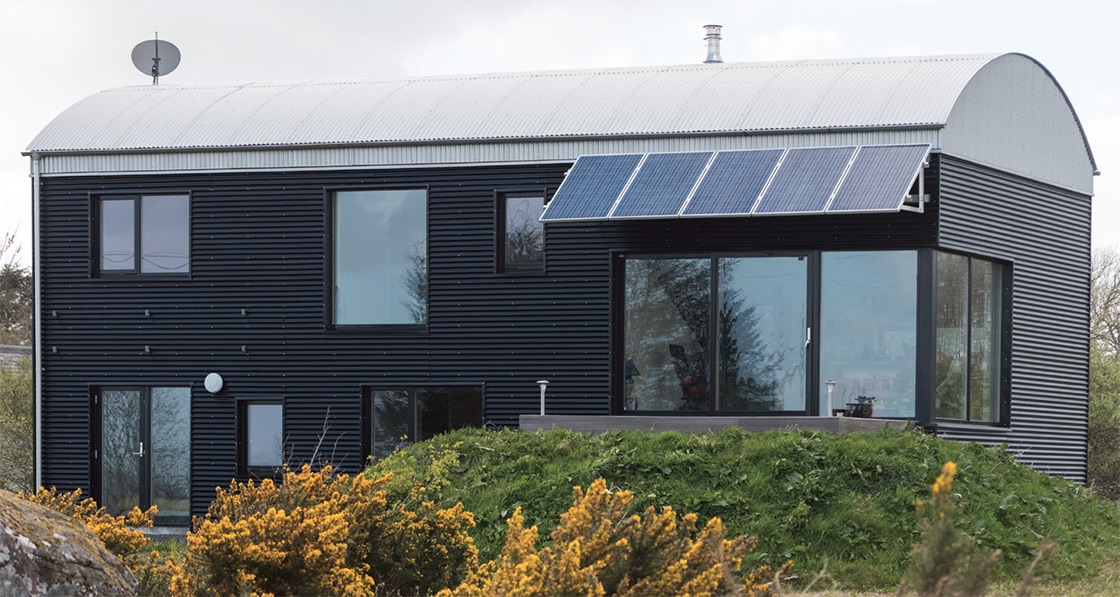
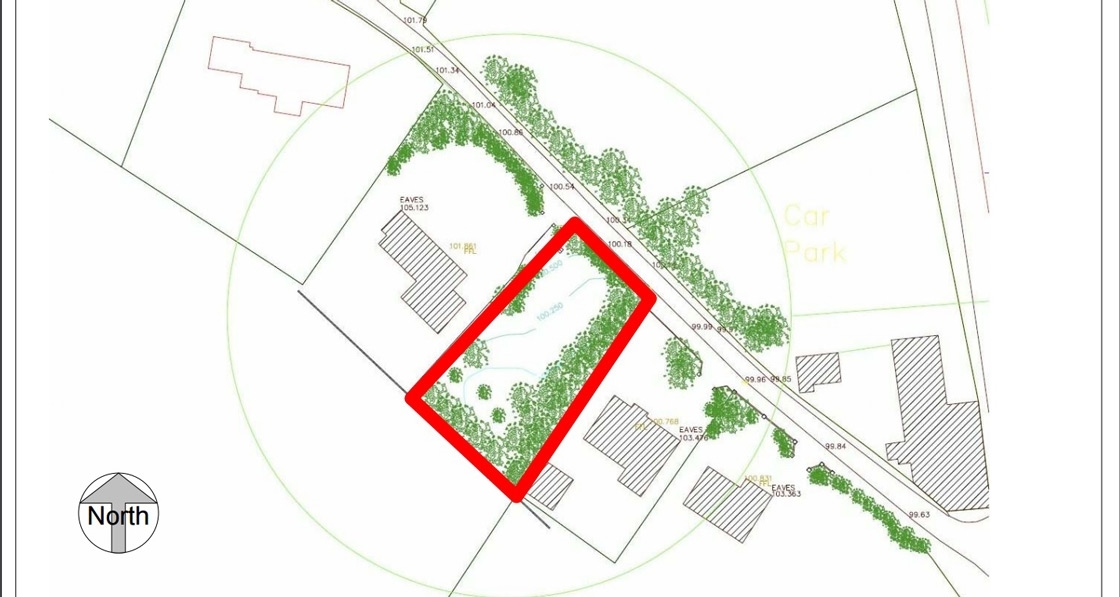
Ground-breaking housing scheme captures one developer’s journey to passive
The just-finished second phase of Durkan Residential’s ambitious Silken Park scheme in south-west Dublin bridges the gap between two extremes: while phase one was built to the 2002 building regulations, phase three — which will break ground next year — will comprise 59 passive certified units.